AIDMA vs AISAS:
Key Differences in Customer Journey Models
2023/01/19

AIDMA vs AISAS: Understanding the Differences in Customer Journeys Through Two Research Perspectives
AIDMA is one of the models that explains the process of consumer behaviour. AIDMA is an acronym for Attention, Interest, Desire, Memory, and Action. The AIDMA model focuses on behaviour leading up to the action phase i.e., customer's purchase of the product or service.
AIDMA is a consumer behaviour model first introduced by advertising specialist Samuel Roland Hall in his 1924 book, Retail Advertising and Selling. It was used as the basis of marketing practice until the AISAS model came along.
To summarise each phase of the AIDMA model:
- Attention: the customer gets to know about your product through an advertisement.
- Interest: the customer is interested in the product.
- Desire: customer wants the product.
- Memory: the feeling or emotion of wanting the product is engraved in memory.
- Action: purchase of the product.
AIDMA is more of a linear model of consumer behaviour because it was introduced before the advent of the internet. An overview of the AIDMA model will be something like this—a product captures the customer's attention, the customer develops an interest and desire for the product and remembers it before proceeding to a store for purchase (action phase).
AIDMA vs AISAS
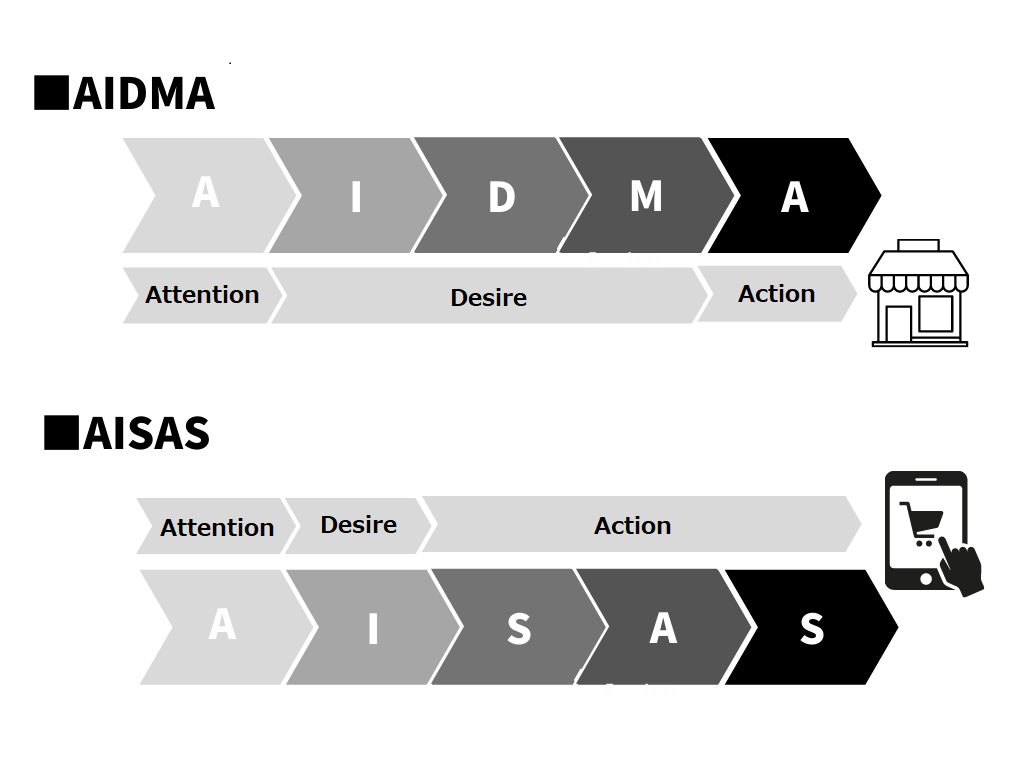
After the launch of the internet into society, the AISAS model was introduced in 2004. There are three significant differences between AIDMA and AISAS, which are as follows:
- Is there a search phase involved?
- Does it need to be committed to memory?
- Is the consumer’s opinion important after the product has been purchased? (sharing phase in the AISAS model/product reviews)
Searching for and purchasing a product has become much easier with the internet. The post-purchase product review has also become very important for businesses to attract potential new customers. These phases were absent when the AIDMA model was introduced to marketing practice.
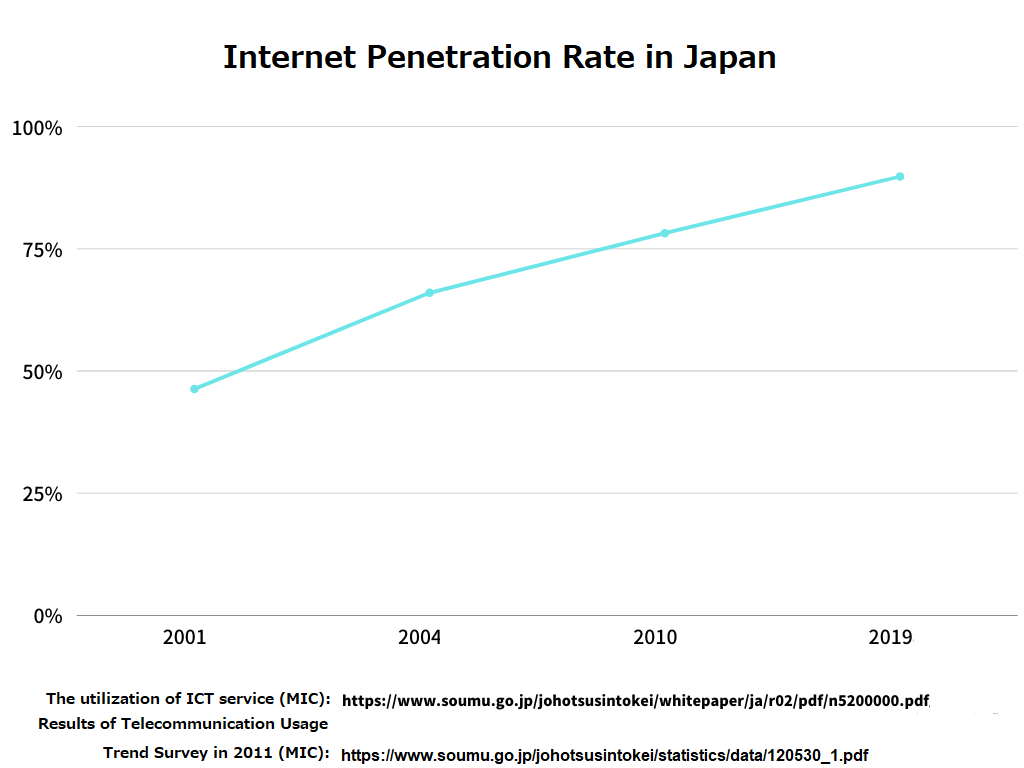
As shown in the graph above, there were about 46.3% of Japanese internet users in Japan in 2001. That number increased to 66% in 2004 when the AISAS model was proposed. The number of internet users after 2004 has continued to grow, explaining the relevance and prevalence of the AISAS model. Judging by the statistics above, and consumer preference for searching for a product on the Internet, it is clear why the AISAS model is preferred to AIDMA when it comes to understanding contemporary consumer behaviour.
However, AIDMA is still relevant in traditional advertising of simple products, where the objective is for the customer to choose your product over your competitors. In these cases, communication is primarily one-sided, i.e., business to consumer, and the customers do not feel the need to learn beyond what the advertisement states.
The AISAS model is better for web marketing and in cases where communication is two-sided, i.e., between the consumer and the business. This is especially true in cases of social media or social networking services (SNS).
Summary
AISAS is widely used as the model depicting consumer behaviour in the digital era. However, depending on where the customer base of the company's products is, the AISAS model may not be suitable. In these cases, customer behaviour models such as AIDMA can be the better choice.
The general framework of the customer journey map is still drawn on the AIDMA and AISAS models. However, the customer journey map accounts for the customer's emotions and feelings towards a brand. In other words, the customer journey map still uses the AIDMA and AISAS models as a foundation. The map incorporates the emotional aspects of consumer behaviour to accommodate the changes that connectivity and the internet have created.
Beginner's Guide to Successful Online Survey
 |
Using online surveys is a quick and cost-effective way to understand your target consumer and build right strategies. |

