Crafting Effective Survey Questionnaires:
A Step-by-Step Guide Part1
2023/11/02

How to Create Survey Questionnaires in 2023 for Market Research
Market research is pivotal for businesses aiming to navigate in our evolving commercial landscape. Surveys, as a cornerstone of this research, allow for the collection of vital data. This guide offers you a focused approach to designing effective survey forms, emphasising the importance of a well-crafted questionnaire. Whether presented digitally or in print, the design quality of the questionnaire directly influences the accuracy and reliability of the insights obtained. This makes good design indispensable for businesses, especially those venturing into market research for the first time.
Before plunging into the stream of survey design, it's worth clarifying a few things. What exactly constitutes a survey? And how does it tie in with market research? Interestingly, the word "questionnaire" traces its roots to the French word "enquête", synonymous with "investigation", "inquiry", or "exploration". This bears a close resemblance to the English definition of “research”. In Japan, for instance, "questionnaires" are more frequently associated with large-scale quantitative surveys and are seldom used for qualitative pursuits, such as interviews. For the purposes of this article, the focus will be on large surveys that use standardised questionnaires.
Understanding the Survey Design Process
For businesses launching their first survey, the following considerations are relevant, you will need to:
- Identify the main questions to feature.
- Decide on the number of choices for each question.
- Determine the ideal survey length.
- Recognize and avoid common mistakes.
There are many aspects in the field of market research that may seem complex or unclear. It is said that "surveys are all about the questionnaire", therefore the design of the questionnaire holds significant importance in market research.
Steps to Design an Effective Survey
Creating an effective survey demands a systematic approach. This guide provides an in-depth breakdown of the nine crucial steps to devising surveys that prove to be not only impactful but also align with your business goals. Each step is designed to ensure clarity, accuracy, and relevance in survey outcomes:
Step 2: Choosing the Survey Format and Collection Method.
Step 3: Identifying Individual Questions.
Step 4: Selecting the Answer Format for Questions.
Step 5: Determining Question Wording.
Step 6: Organising the Sequence of Questions.
Step 7: Defining Specifics—Survey Layout and the Number of Questions.
Step 8: Reviewing and Refining the Previous Steps.
Step 9: Conducting a Pretest.
(While this structure is useful, it's flexible as well, and can be adapted to fit specific needs.)
Step 1: Deciding What Information to Collect
When initiating the survey design, it's fundamental to clearly define the primary goals of that piece of research, and delve into the motivations behind the research
Things to clarify before crafting a survey:
- Why do we need to conduct this research in the first place?
- What are the current marketing challenges?
- What insights are expected from the survey?
- What actions will be influenced by the survey results?
Without this foundational understanding, interpreting the survey results could be confusing and possibly make the data seem unhelpful in addressing the core challenges. Thus, avoiding an ambiguous survey design is key.
Recommended techniques to organising the groundwork:
- Chronological Organisation: Outline the timeline of the theme under investigation.
- Brainstorming Causes and Factors: Examine and identify the primary causes and factors behind the challenge at hand.
- Tree Diagram: Pose iterative "Why?" questions to deepen understanding, like exploring reasons behind declining sales.
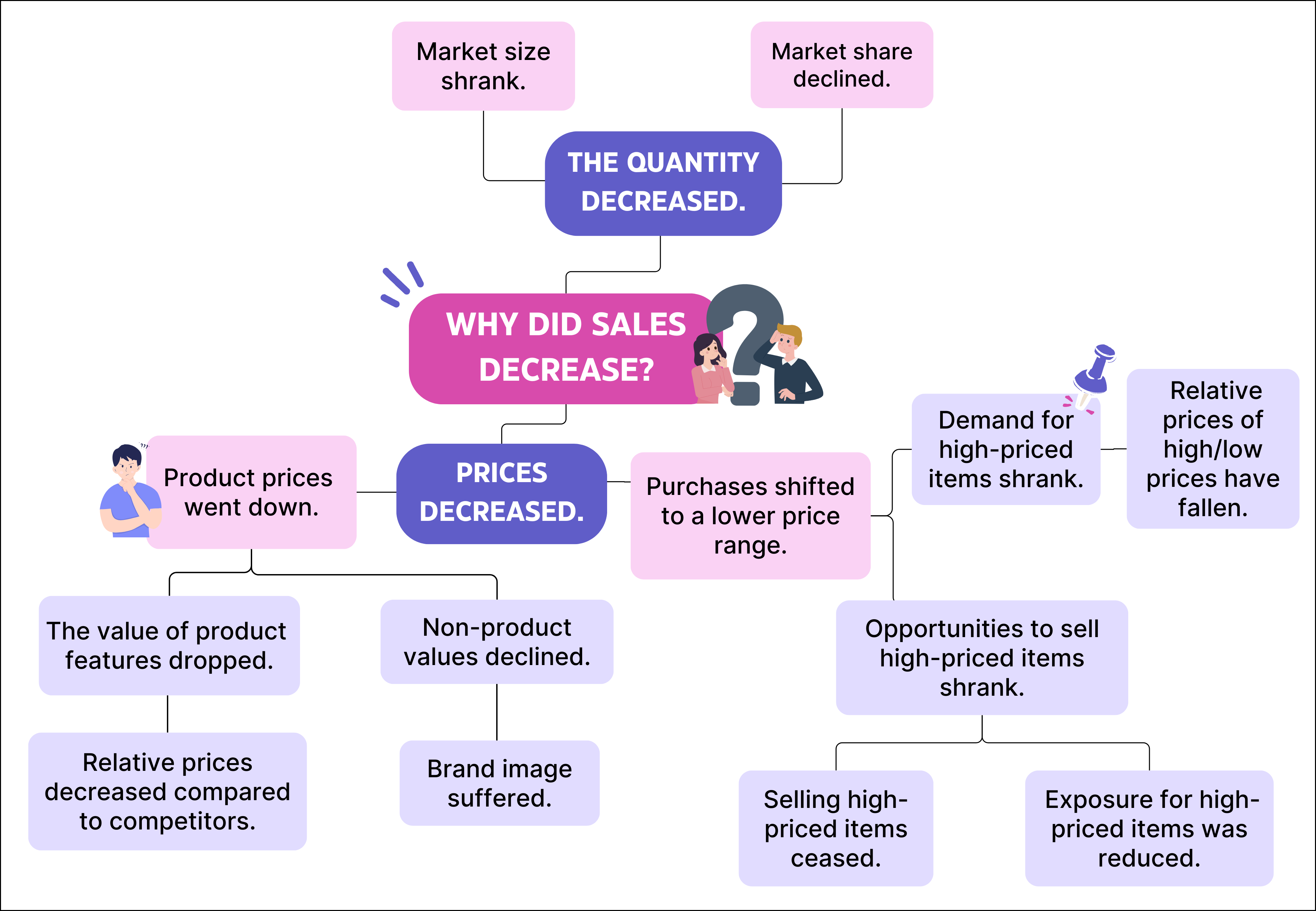
*Example of a tree diagram that deepens the "why" of "Why did sales decline?”
These techniques provide a well-rounded and multi-faceted view of the information. Fresh insights can emerge, and occasionally, there might be a need to hone or pivot the research direction.
While gathering this information, hypotheses related to the research theme should be developed. For instance:
- Has the brand's appeal decreased because its packaging colour is no longer as distinct as that of its competitors?
- Even if other brands provide 500ml options, is there a noticeable trend where these sizes are seldom selected?
- Could shifts in societal habits be causing an older age group to visit restaurants and bars more frequently?
By posing such hypotheses, businesses can design their survey questionnaires to specifically address these assumptions, ensuring the data gathered is relevant and actionable.
Step 2: Choosing the Survey Format and Collection Method
Determining the appropriate survey type and collection method is also foundational to effective survey execution. While online surveys have gained traction due to their time-efficiency and affordability, alternative methods, such as central location test (venue-based research), might be more relevant for you, depending on the research's focus and target audience.
It's important to recognize potential response biases tied to different survey methods. For instance, online surveys might underrepresent older demographics who infrequently use the internet. Therefore, it is imperative to select a collection method that aligns with the desired respondent profile.
When considering respondent criteria, several factors should be evaluated:
- Demographic Information: This includes attributes such as region, gender, age, occupation, marital status, presence of children, annual income, among others.
- Behaviour/Attitude Data: This encompasses aspects like product/service awareness, usage patterns, and discontinuation reasons.
- Psychological Insights: Factors such as values, lifestyles, and personal preferences fall under this category.
While it might seem ideal to be very specific in determining respondent criteria to gain deeper, hypothesis-focused insights, it's essential to strike a balance. Over-narrowing criteria could result in challenges in securing an adequate sample size, or yield results too specialised for broader marketing strategies. The aim should be to determine and evaluate vital criteria that support hypothesis validation.
Step 3: Identify Individual Questions
This stage involves converting the hypotheses, established in Step 1, into tangible question items that shape the survey. These questions should directly reflect the survey's core objectives, aiming to yield insightful and actionable data.
When formulating these questions, it's imperative to:
- Stay Relevant to Hypotheses: For example, if the hypothesis is that a brand's declining popularity is due to less attractive packaging compared to its competitors, questions could include:
- "Between Company A and Competitor B, which packaging design appeals more to you?"
- "For those preferring Competitor B, what aspects of Company A's design are less appealing?"
- Limit the Number of Questions: While it is important to gather comprehensive data, an excessive number of questions will often overwhelm respondents and compromise data quality.
- Uphold Respondent Privacy: Ensure questions do not unintentionally identify individuals. For example, while singular questions about "age" or "department" might be simple, combining them could pinpoint specific individuals. Additionally, refrain from probing into sensitive personal details, like home addresses, academic institutions, company names, medical histories, and so forth, without explicit consent. Furthermore, always seek consent before gathering digital behaviour histories, such as browsing activities, location data, and email histories.
Prioritising the respondent's comfort and privacy is crucial to ethical survey design and fosters important trust.
Step 4: Selecting the Answer Format for Questions
The choice of answer format plays a crucial role in the type and quality of responses received. There are various answer formats, including:
- Single Answer (SA)
- Multiple Answers (MA)
- Free Answers (FA)
- Limited Answer (LA)
- Matrix (options range from SA, MA, pulldown, FA, and more)
While determining the format:
- Consider Respondent Experience: Some formats, particularly matrix questions or open-ended responses, can be challenging for smartphone users, potentially leading to higher dropout rates. It is essential to strike a balance between obtaining comprehensive data and also not overwhelming your respondents.
- Ensure Clarity in Options: Carefully curate options to avoid situations where respondents feel they have nothing to choose from or are confused by overlapping answers. For single-answer formats, ensure choices are clear, distinct, and mutually exclusive.
- Optimise Choice Design:
- Avoid having too many, or too few, choices.
- Use wording that is universally understood to avoid varied interpretations.
- Quantify answers where possible.
- Keep option lengths concise.
- Seek feedback from a diverse group to ensure the options cater to a broader audience.
- Incorporate dummy options to identify and filter out careless or random answers.
Prioritising clarity, simplicity, and respondent ease ensures higher engagement, reduces ambiguity, and improves the overall quality of data collected.
Summary
This first part has covered the first four steps of survey questionnaire creation. Each step serves as a foundation towards developing a survey aligned with set objectives and collecting precise, actionable data. Yet, this progression is not complete.
In the upcoming article, "Crafting the Perfect Survey Questionnaire: Part 2," the focus will shift to the final five steps of this procedure. From refining question phrasing to executing a pretest, the next article will delve into the concluding stages of this systematic strategy, ensuring the survey is well positioned for optimal results.
Beginner's Guide to Successful Online Survey
 |
Using online surveys is a quick and cost-effective way to understand your target consumer and build right strategies. |

